Microsoft Excel is a powerful tool used by millions worldwide for data analysis, financial modeling, and much more. Mastering Excel formulas can significantly enhance your productivity and efficiency. This article will guide you through some of the top Microsoft Excel formulas that you should learn to maximize your potential with this versatile software.
Basic but Powerful Formulas
XLOOKUP (The Modern VLOOKUP Replacement)
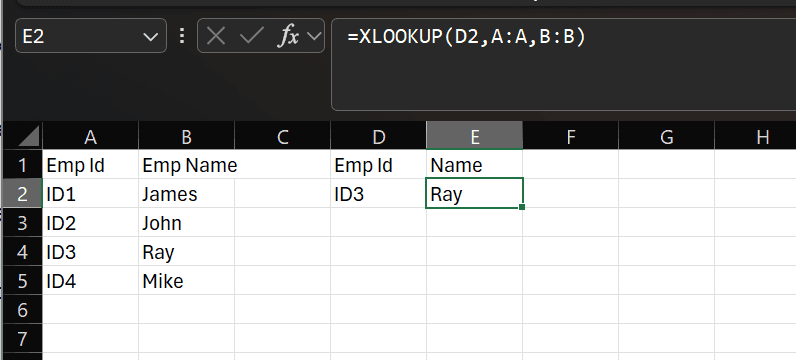
For Example Cell A1: Employee ID
and Cell B1: Employee Name
Syntax =XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array, [if_not_found], [match_mode], [search_mode])
Function =XLOOKUP(D2,A:A,B:B)
What we did, we asked (lookup_value as D2 cell), to find it in A Column (Lookup array), return with B Column’s value (return_array) and it returned with value as Ray in our above screenshot.
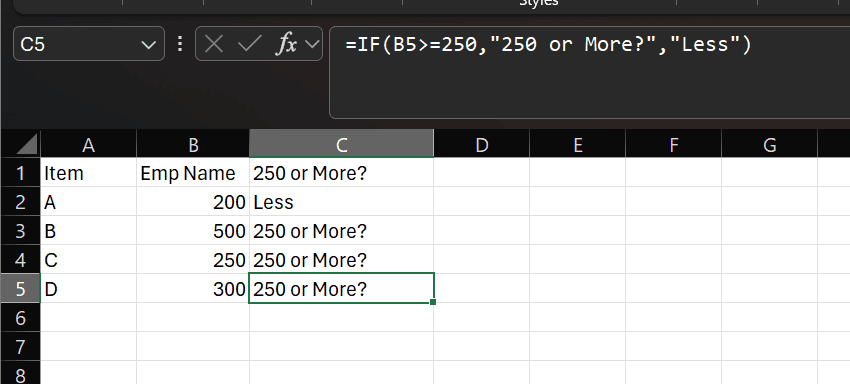
IFS (Multiple Conditions)
Syntax: =IFS(logical_test1, value_if_true1, logical_test2, value_if_true2, ...)
Real-life Example:
Intermediate Level Formulas
FILTER (Dynamic Data Filtering)
Syntax: =FILTER(array, include, [if_empty])
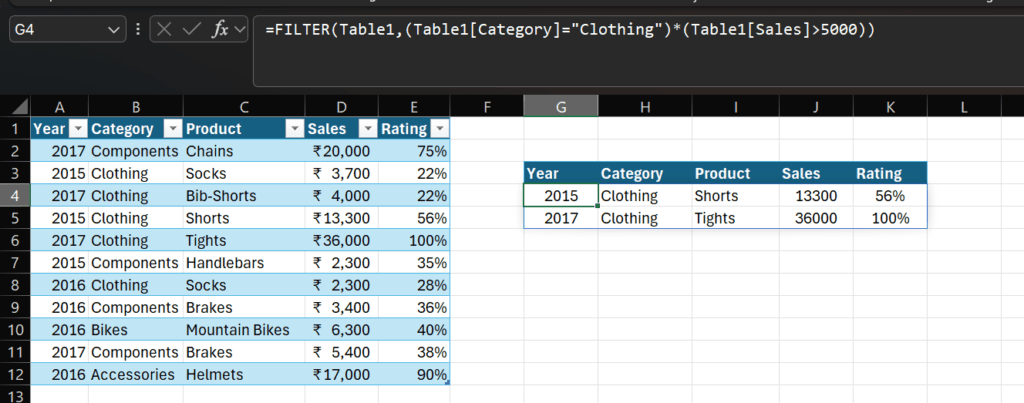
In the above example using this > =FILTER(Table1,(Table1[Category]=”Clothing”)*(Table1[Sales]>5000))
I have filtered Clothing category with above 5000 sales, and it results in 2 matching entries.
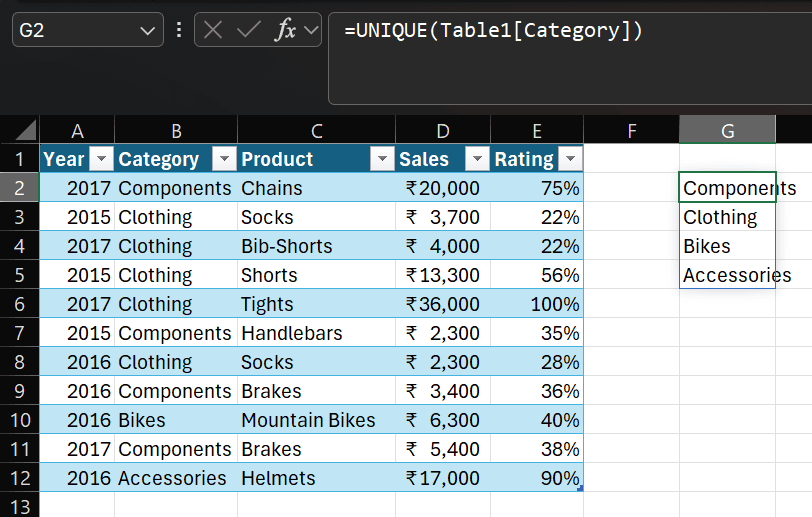
UNIQUE (Remove Duplicates)
Real-life Example:
Syntax: =UNIQUE(array, [by_col], [exactly_once])
Advanced Analytics Formulas
SEQUENCE (Generate Arrays Dynamically)
- Syntax: =SEQUENCE(rows, [columns], [start], [step])
- Use Case: SEQUENCE is perfect for generating dynamic arrays of numbers for analysis or simulations.
- Example: =SEQUENCE(5, 1, 1, 2) generates a column of 5 numbers starting at 1 and increasing by 2 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9).
LET (Simplify Complex Formulas)
- Syntax: =LET(name1, value1, [name2], [value2], …, calculation)
- Use Case: LET allows you to define variables within a formula, making complex calculations easier to read and maintain.
- Example: =LET( sales, A1:A10, tax_rate, 0.1, total_tax, SUM(sales) * tax_rate, total_tax ) This calculates the total tax for a range of sales values.
LAMBDA (Custom Functions)
- Syntax: =LAMBDA(parameter1, parameter2, …, calculation)(input1, input2, …)
- Use Case: LAMBDA lets you create reusable custom functions directly in Excel.
- Example:
Define a custom function for calculating compound interest: =LAMBDA(principal, rate, periods, principal * (1 + rate)^periods)(1000, 0.05, 10) This calculates the future value of $1,000 at a 5% annual interest rate over 10 years.
New Features in 2024
Dynamic Array Enhancements
- Microsoft continues to improve dynamic arrays, enabling more intuitive and powerful formulas like TEXTSPLIT and TEXTJOIN.
- Example: Use TEXTSPLIT to break a string into an array =TEXTSPLIT(“Excel,Formulas,2024”, “,”) This splits the string into “Excel”, “Formulas”, and “2024”.
IMAGE Function
- Syntax: =IMAGE(source, [alt_text], [sizing], [height], [width])
- Use Case: Insert images directly into cells, making dashboards and reports more visually appealing.
- Example:excelCopy=IMAGE(“https://example.com/logo.png”, “Company Logo”)
Expanded AI Integration
- Excel’s AI now suggests formulas, automates repetitive tasks, and integrates with Power BI more seamlessly.
Real-world Applications
Financial Modeling
- Use
XLOOKUP,LET, andLAMBDAto build dynamic and scalable financial models. - Example: Calculate loan repayments using
PMTcombined withLETfor cleaner formulas.
Data Cleaning
- Combine
UNIQUE,FILTER, andTEXTSPLITto clean and organize large datasets. - Example: Remove duplicates and filter rows matching certain criteria in one step.
Sales Dashboards
- Leverage
SEQUENCE,IMAGE, andSPARKLINEto create visually appealing and interactive sales dashboards.
Tips and Best Practices
- Master Dynamic Arrays: Learn how to use dynamic array formulas like
FILTER,SORT, andUNIQUEto simplify your workflow. - Use Named Ranges: Use named ranges or the
LETfunction to make formulas easier to read. - Error Handling: Always include error handling with
IFERRORorIFNAto make your formulas robust. - Document Your Work: Add comments to complex formulas or use
ALT+ENTERto break them into readable lines. - Stay Updated: Regularly explore new Excel features and updates to stay ahead.
Microsoft Excel Shortcuts Keys
Excel Shortcuts Comprehensive Guide
Microsoft Excel Shortcuts download for productivity
This guide provides an extensive list of keyboard shortcuts to enhance your efficiency in Microsoft Excel. The shortcuts are categorized into logical sections and organized into tables with clear headers and subheaders for easy reference.
Table 1: Basic Function Keys
| Function Key | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | Open Help | Launches Microsoft Excel Help |
| F2 | Edit Cell | Puts the cursor at the end of the active cell |
| F3 | Paste Name | Opens the Paste Name dialog |
| F4 | Repeat/Toggle | Repeats the last action or toggles cell reference types |
| F5 | Go To | Opens the Go To dialog box |
| F6 | Navigate Panes | Cycles through split panes |
| F7 | Spell Check | Opens the Spelling dialog box |
| F8 | Extend Selection | Toggles selection extension mode |
| F9 | Recalculate | Recalculates all worksheets |
| F10 | Menu Activation | Activates the Menu Bar |
| F11 | Create Chart | Generates a chart on a new chart sheet |
| F12 | Save As | Opens the Save As dialog box |
Table 2: Modified Function Keys
Shift-Modified Function Keys
| Key Combination | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Shift+F2 | Edit/Insert Comment | Inserts or edits a cell comment |
| Shift+F3 | Insert Function | Opens the Insert Function dialog |
| Shift+F4 | Repeat Find | Repeats the last Find action |
| Shift+F5 | Find Dialog | Opens the Find dialog box |
| Shift+F6 | Navigate Backward | Moves to the previous pane in split view |
| Shift+F8 | Toggle Add Mode | Switches Add Mode for multiple selections |
| Shift+F9 | Recalculate Sheet | Recalculates only the active worksheet |
| Shift+F10 | Context Menu | Displays the context (shortcut) menu |
| Shift+F11 | New Worksheet | Inserts a new worksheet before the current sheet |
| Shift+F12 | Save/Save As | Saves the workbook or opens Save As if unsaved |
Control-Modified Function Keys
| Key Combination | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Ctrl+F1 | Toggle Ribbon | Collapses or expands the Ribbon |
| Ctrl+F2 | Print Preview | Opens the Print Preview window |
| Ctrl+F3 | Name Manager | Opens the Name Manager dialog box |
| Ctrl+F4 | Close Workbook | Closes the current workbook window |
| Ctrl+F5 | Restore Window | Restores the active workbook window’s size |
| Ctrl+F6 | Switch Workbook | Moves to the next open workbook |
| Ctrl+F7 | Move Window | Activates the Move command |
| Ctrl+F8 | Resize Window | Activates the Resize command |
| Ctrl+F9 | Minimize Window | Minimizes the active workbook window |
| Ctrl+F10 | Maximize Window | Maximizes the active workbook window |
| Ctrl+F12 | Open File | Opens the Open dialog box |
Table 3: Editing & Formatting Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Action | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Ctrl+C | Copy | Editing |
| Ctrl+X | Cut | Editing |
| Ctrl+V | Paste | Editing |
| Ctrl+Z | Undo | Editing |
| Ctrl+Y | Redo | Editing |
| Ctrl+S | Save | File Management |
| Ctrl+P | File Management | |
| Ctrl+N | New Workbook | File Management |
| Ctrl+O | Open Workbook | File Management |
| Ctrl+W | Close Workbook | File Management |
| Ctrl+B | Bold | Formatting |
| Ctrl+I | Italic | Formatting |
| Ctrl+U | Underline | Formatting |
| Ctrl+1 | Format Cells Dialog | Formatting |
Table 4: Navigation & Selection Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Action | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Arrow Keys | Move between cells | Standard cell-to-cell navigation |
| Tab / Shift+Tab | Move right / left | Navigates horizontally through cells |
| Enter / Shift+Enter | Move down / up | Navigates vertically through cells |
| Home | Start of row | Jumps to the first cell in the current row |
| Page Up / Page Down | Scroll screen | Moves the view one screen up or down |
| Ctrl+Arrow Keys | Jump to data edge | Skips to the boundary of a data region |
| Ctrl+Home | Go to A1 | Moves directly to cell A1 |
| Ctrl+End | Last used cell | Jumps to the bottom-right used cell |
| Shift+Arrow Keys | Extend selection | Expands selection one cell at a time |
| Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Keys | Extend selection to data edge | Selects cells to the edge of the data region |
Table 5: Additional Useful Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Action | Additional Info |
|---|---|---|
| Ctrl+Shift+L | Toggle Filters | Enables/disables filters on selected ranges |
| Ctrl+T | Convert Range to Table | Formats a selected range as a table |
| Ctrl+’ | Copy from Above | Copies content from the cell immediately above |
| Ctrl+R | Fill Right | Fills cells to the right with the content from the leftmost cell |
| Ctrl+D | Fill Down | Fills cells downward with the content from the top cell |
| Ctrl+` | Toggle Formula View | Switches between displaying formulas and their results |
| Ctrl+Shift+Enter | Array Formula Entry | Confirms an array formula entry |
Conclusion
Mastering Microsoft Excel formulas is a game-changer for anyone working with data. From basic to advanced levels, these formulas empower you to analyze, visualize, and manage data efficiently. By incorporating new features and best practices, you can take your Excel skills to the next level and unlock its full potential. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, there’s always something new to learn in Excel!


You need to be a part of a contest for one of the most useful blogs on the
internet. I’m going to recommend this site!
Hello, just wanted to mention, I loved this post. It was inspiring.
Keep on posting!